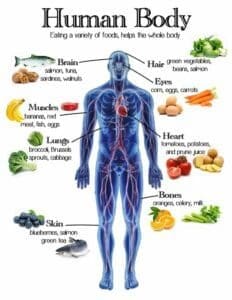
Embark on a journey towards optimal health with our ‘Healthy Eating Guide: Nutritionist-Approved Foods.’ This guide, enriched with expertise from seasoned nutritionists, provides you with essential knowledge to make well-informed dietary choices. Dive into the world of nutritious fruits and vegetables, discover the benefits of whole grains and lean proteins, and explore a variety of tasty, healthful food options. This comprehensive article is your pathway to a balanced diet that not only fuels your body but also leaves you feeling energized and fulfilled.
Nutrient-Dense Foods
Eating nutrient-dense foods is essential for maintaining good health and providing our bodies with the necessary vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These foods help us thrive and keep our bodies functioning optimally. In this article, we will explore the various categories of nutrient-dense foods and learn how to incorporate them into our daily diet.
Fruits and Vegetables
No healthy eating guide would be complete without emphasizing the importance of fruits and vegetables. These colorful and delicious foods are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. They provide us with a wide range of nutrients that are vital for our overall well-being.
Whole Grains
Whole grains are another crucial component of a well-balanced diet. Unlike refined grains, which have been stripped of their nutritional value, whole grains retain all parts of the grain, including the bran, germ, and endosperm. This means that they are rich in fiber, B vitamins, and minerals.
Lean Proteins
Protein is an essential macronutrient that plays a crucial role in building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and maintaining a healthy immune system. Choosing lean proteins ensures that we get the necessary nutrients without excessive saturated fats.
Healthy Fats
Contrary to popular belief, fats are not all bad. In fact, healthy fats are an integral part of a balanced diet. They provide energy, support cell growth, and help absorb certain vitamins. Incorporating healthy fats into our meals can promote heart health and improve brain function.
Dairy and Dairy Alternatives
Dairy products are known for their high calcium content, which is essential for strong bones and teeth. However, some individuals may be lactose intolerant or choose to follow a plant-based diet. In such cases, there are plenty of dairy alternatives available that provide similar nutrients.
The Power of Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are not only colorful and delicious, but they also offer a wide range of health benefits. These plant-based foods are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them an excellent choice for maintaining optimal health.
Colorful Choices
When it comes to fruits and vegetables, the more colorful, the better. Each vibrant hue corresponds to different nutrients, so it’s essential to consume a variety of colors. For example, orange fruits and vegetables, such as carrots and sweet potatoes, are rich in beta-carotene, while leafy greens are packed with iron and calcium.
Superfoods
Certain fruits and vegetables are considered “superfoods” due to their exceptionally high nutrient content. Blueberries, kale, spinach, and broccoli are all excellent examples. These superfoods are known to provide a wide array of health benefits, including improved brain function, enhanced immune systems, and reduced inflammation.
Buy Fresh or Frozen
Eating fresh fruits and vegetables is always a great choice, but frozen options can be just as nutritious. In fact, frozen fruits and vegetables are typically frozen at their peak ripeness, retaining their nutrients. They are also convenient and last longer, making it easier to incorporate them into our meals.
Whole Grains for a Well-Balanced Diet
Whole grains are an essential part of a healthy and well-balanced diet. They are packed with fiber, vitamins, minerals, and complex carbohydrates, providing sustained energy and promoting digestive health.
Understanding Whole Grains
Whole grains are grains that have not undergone processing that removes the bran and germ. This means that they contain all parts of the grain, including the fiber-rich bran and nutrient-dense germ. Examples of whole grains include whole wheat, oats, brown rice, quinoa, and barley.
Whole Grain Options
Incorporating whole grains into our diet can be as simple as swapping refined grain products with their whole grain counterparts. Opt for whole wheat bread instead of white bread, choose brown rice over white rice, and try out different whole grain pasta options.
Portion Control
While whole grains are beneficial, it’s important to consume them in moderation. Portion control plays a key role in maintaining a balanced diet. Aim for around one-fourth of your plate to be filled with whole grains, and be mindful of your overall calorie intake.
Lean Proteins for Muscle Health
Proteins are the building blocks of our body and play a crucial role in muscle growth and repair. Choosing lean sources of protein ensures that we get the necessary nutrients without excessive saturated fats.
Poultry
Poultry, such as chicken and turkey, are excellent sources of lean protein. They are low in fat, high in essential amino acids, and packed with vitamins and minerals. Grilled, baked, or roasted, poultry can be a healthy and delicious addition to any meal.
Fish and Seafood
Fish and seafood are not only rich in protein but also contain heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids are known to reduce inflammation, improve brain health, and promote heart health. Incorporating fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and sardines into our diet can provide numerous health benefits.
Legumes and Beans
Legumes and beans are a fantastic plant-based source of protein. Additionally, they are high in fiber, which aids in digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Black beans, chickpeas, lentils, and kidney beans are just a few examples of legumes that can be incorporated into various dishes.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are not only packed with protein but also contain healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals. Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are all excellent choices. Sprinkle them on salads, add them to smoothies, or enjoy them as a snack for a nutrient-dense boost.
Healthy Fats for a Heart-Healthy Diet
Including healthy fats in our diet is essential for heart health and overall well-being. Healthy fats provide energy, support cell growth, and help absorb certain vitamins.
Avocados
Avocados are not only delicious but also rich in monounsaturated fats, which can help improve cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. They are also packed with fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Add slices of avocado to salads, sandwiches, or enjoy it as guacamole.
Olive Oil
Olive oil is a staple in many Mediterranean diets and is known for its heart-healthy benefits. It is high in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, which can help reduce inflammation and improve heart health. Use olive oil as a dressing for salads or as a healthy cooking oil.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds, are not only excellent sources of plant-based protein but also contain healthy fats. They can be enjoyed as a snack, added to salads, or used in baking to provide a dose of healthy fats.
Fatty Fish
Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and trout, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids have been shown to reduce inflammation, improve brain function, and promote heart health. Aim to include fatty fish in your diet at least twice a week.
Dairy and Dairy Alternatives for Calcium Intake
Dairy products are well-known for their high calcium content, which is essential for strong bones and teeth. However, for those who are lactose intolerant or following a plant-based diet, there are plenty of dairy alternatives available.
Dairy Options
If you can tolerate dairy, incorporating low-fat or fat-free options into your diet can provide a good source of calcium. Milk, yogurt, and cheese are all rich in calcium. Choose options that are low in added sugars and unhealthy fats.
Plant-Based Alternatives
For those who cannot consume dairy, there are numerous plant-based alternatives available. Almond milk, soy milk, and oat milk are just a few examples. These alternatives are often fortified with calcium to ensure you meet your daily requirements.
Fortified Alternatives
Some dairy alternatives are fortified with calcium and other essential nutrients. Be sure to check the labels to ensure they contain adequate amounts of calcium and other nutrients. Consider fortified yogurt alternatives, cheeses, and other products to meet your calcium needs.
Balancing Macronutrients
Understanding macronutrients and how to balance them is key to maintaining a healthy and well-rounded diet.
Understanding Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the three main types of nutrients that our bodies require in large amounts: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each macronutrient plays a unique role in our overall function, and it’s crucial to understand their importance.
Caloric Needs
The number of calories we need each day varies based on factors such as age, gender, activity level, and overall health. Understanding our caloric needs helps ensure we consume an appropriate amount of macronutrients. Consulting with a nutritionist or using online tools can help determine your specific caloric needs.
The Plate Method
To achieve a well-balanced meal, one helpful tool is the plate method. Divide your plate into sections: half of the plate should consist of fruits and vegetables, one-fourth should be lean proteins, and one-fourth should be whole grains or complex carbohydrates. This method allows for a balanced intake of macronutrients.
Healthy Snack Choices
Choosing healthy snacks is essential for maintaining energy levels throughout the day and avoiding unhealthy cravings.
Fresh Fruits and Vegetables
Fresh fruits and vegetables make excellent snack choices. They are high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and can be enjoyed on their own or paired with a healthy dip or hummus.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are not only satiating but also contain healthy fats, protein, and fiber. A small handful of almonds, walnuts, or pumpkin seeds can provide a nutrient-rich and satisfying snack.
Yogurt and Cottage Cheese
Low-fat or Greek yogurt and cottage cheese are high in protein and calcium. They can be enjoyed plain or topped with fresh fruits or nuts for added flavor and nutrients.
Hydration and Water Intake
Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and well-being. Water is involved in numerous bodily functions and aids in digestion, circulation, and temperature regulation.
Importance of Hydration
Proper hydration is vital for maintaining healthy bodily functions. It aids in digestion, nutrient absorption, and waste removal. Staying hydrated can also help prevent fatigue, improve concentration, and promote healthy skin.
Water Recommendations
Water requirements vary based on factors such as age, activity level, and climate. As a general guideline, aim to drink at least eight cups (64 ounces) of water per day. Be sure to adjust your intake based on individual needs and consult with a healthcare professional if you have specific hydration concerns.
Hydrating Foods
In addition to drinking water, certain foods can also contribute to hydration. Fruits such as watermelon, oranges, and grapes, as well as vegetables like cucumbers and celery, have high water content and can help meet your hydration needs.
Mindful Eating Habits
Practicing mindful eating habits can help us establish a healthy relationship with food, promote portion control, and reduce overeating.
Portion Control
One of the most crucial aspects of mindful eating is portion control. Understanding appropriate portion sizes and being mindful of our hunger and fullness cues can help prevent overeating and promote a balanced intake of all nutrients.
Slow and Enjoyable Eating
Eating slowly and savoring each bite can enhance our enjoyment of food and help us tune in to our body’s hunger and fullness signals. Engage all your senses while eating, and take the time to appreciate the flavors, textures, and aromas of your meals.
Reducing Distractions
Eating while distracted, such as watching TV or scrolling through our phones, can lead to mindless eating and overconsumption. By reducing distractions and focusing on our meals, we can better connect with our hunger and fullness cues and make healthier choices.
Incorporating nutrient-dense foods into our diet is crucial for maintaining good health and overall well-being. By focusing on fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and dairy or dairy alternatives, we can ensure that our bodies receive the necessary nutrients. By practicing mindful eating habits, staying hydrated, and choosing healthy snack options, we can support our bodies’ optimal functioning. So let’s make a conscious effort to fuel ourselves with nutrient-dense foods and prioritize our health!
Disclaimer
The content is purely informative and educational in nature and should not be construed as medical advice. Please use the content only in consultation with an appropriate certified medical or healthcare professional